What are ED medications?
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common problem among males involving an inability to achieve or maintain an erection. Medications have been developed to treat this condition. They work in part by promoting dilation of the blood vessels in the penis. This same dilation of the blood vessels also occurs in other parts of the body. Facial flushing, stuffy nose, and headache may result from vascular dilation in the head. A decrease in blood pressure may also occur due to pooling of blood in the larger dilated veins of the body. This drop in blood pressure may cause symptoms of insufficient blood flow, especially in patients with hardening of the arteries.
How can ED medications affect my eyes?
Medications prescribed for erectile dysfunction (ED) may cause temporary blurred vision, light sensitivity, or impaired color vision. If these symptoms occur, a decrease in dosage of medication may be in order. If these symptoms persist, contact your ophthalmologist.
Rarely, a severe permanent decrease in vision may occur after using ED medications…ischemic optic neuropathy. This condition occurs most often in patients with atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and in eyes with crowded optic discs (often seen in far-sighted people). Any sudden decrease in blood pressure (including the use of ED medications) may precipitate ischemic optic neuropathy.
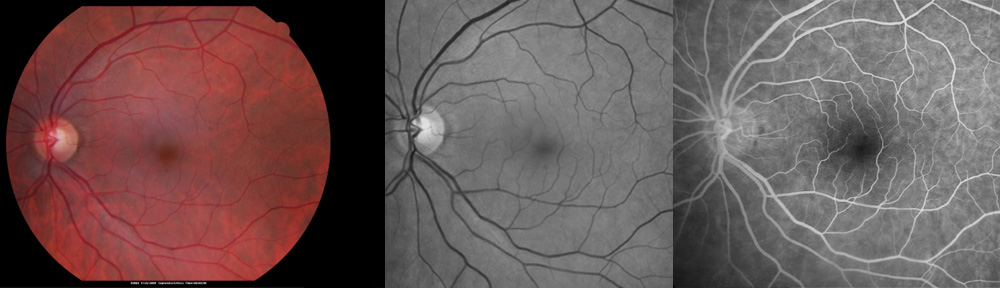
In some patients ED medications might aggravate central serous retinopathy (CSR). a condition more often seen in far-sighted eyes with a thick blood vessel layer in the choroid. This condition causes a round, blurred gray or brown spot in the center of the vision. If this symptom appears while taking ED medications, contact your ophthalmologist.
What other medicines or conditions might interact with ED Medications?
Certain foods and drugs may interact with ED medications. Eating grapefruit or drinking grapefruit juice may affect how your body eliminates ED medications from your body. The following medications should not be used with ED medications: nitrates (nitrogycerin, isosorbide), nitroprusside, certain recreational drugs called “poppers” (which contain amyl or butyl nitrite).
Other medications may also affect ED medications and should be reported to your doctor or pharmacist: prostate medications, blood pressure medications, HIV/AIDS medications, St. John’s wort, some seizure medications, and certain antibiotics.
For a telemedicine consultation with Dr Pautler, please send email request to spautler@rvaf.com. We accept Medicare and most insurances in Florida. Please include contact information (including phone number) in the email. We are unable to provide consultation for those living outside the state of Florida with the exception of limited one-time consultations with residents of the following states: Alabama, Arkansas, Connecticut, Georgia, Minnesota, and Washington.
Copyright © 2017-2022 Designs Unlimited of Florida. All Rights Reserved.