What is multiple sclerosis?
Multiple Sclerosis is a condition of the brain and spinal cord in which there is a loss of the insulating coat of the nerve cells (demyelination). The cause is unknown, but viral and auto-immune causes are suspected along with genetic predisposition. Because the brain controls movement and sensation, multiple sclerosis may cause a variety of symptoms. The symptoms may occur from time to time with normal periods in between (relapsing form). Alternatively, the symptoms may slowly progress and persist over time (progressive form).
How does multiple sclerosis affect the eyes?
Multiple sclerosis may disrupt the nerves that affect the vision or the movement of the eyes. It may also cause inflammation inside the eye. The following are well-recognized problems involving the eyes:
Optic Neuritis: Inflammation of the optic nerve may cause a sudden loss of vision. Often, there is pain in or behind the eye made worse with eye movement.
Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia (INO): An interruption of the nerve fibers that coordinate movement of the two eyes may cause a loss of alignment. If the two eyes are not pointing in the same direction, double vision occurs.
Intermediate Uveitis: A low-grade inflammation inside the eye (vitritis) may cause the slow-onset of fine floating specks in the vision. Over time, the vision may become blurred due to the accumulation of specks, as well as swelling of the retina.
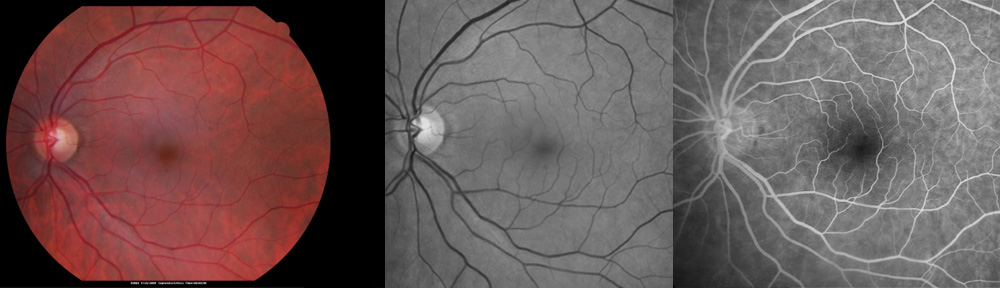
How is multiple sclerosis diagnosed?
When visual symptoms occur, the ophthalmologist may undertake a number of tests in the office to diagnose multiple sclerosis. The optical coherent tomogram (OCT) can identify defects in the optic nerve and diagnose macular edema. Usually, an MRI scan is needed to identify degenerative plaques seen in the brain due to multiple sclerosis. Ultimately, a neurologist is consulted to confirm the diagnosis.
How is multiple sclerosis treated?
A neurologist orchestrates the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Medication and physical therapy help to manage symptoms. There is no cure. The clinical course of multiple sclerosis is variable. The least long-term disability is usually seen in women, those with onset of symptoms early in life, and those with few intermittent symptoms at onset.
The ophthalmologist manages the ocular symptoms. Loss of vision usually returns over time and may be accelerated with the use of IV steroids. Double vision may also improve over time and may be managed by patching one eye.
Intermediate uveitis usually requires medication to prevent progressive permanent loss of vision. Although mild cases may be carefully observed, treatment is needed if floaters interfere with vision or if macular edema (retinal swelling) is present. Steroid medications may be used by pills or by injection. They are best used for short-term management of flare-ups of inflammation. Other non-steroid medications help to suppress the inflammation over the long-term. These medications often require the assistance of a rheumatologist who watches for side effects while the ophthalmologist monitors the inflammation.
For a telemedicine consultation with Dr Pautler, please send email request to spautler@rvaf.com. We accept Medicare and most insurances in Florida. Please include contact information (including phone number) in the email. We are unable to provide consultation for those living outside the state of Florida with the exception of limited one-time consultations with residents of the following states: Alabama, Arkansas, Connecticut, Georgia, Minnesota, and Washington.
Copyright © 2016-2022 Designs Unlimited of Florida. All Rights Reserved.