What is birdshot chorioretinopathy?

Birdshot chorioretinopathy (BSC) is a type of uveitis (pronounced, “you-vee-EYE-tis”), a term used to describe inflammation inside the eye. BSC mainly causes inflammation of the choroid and retina, but may affect other parts of the eye as well. The choroid is the part of the uvea that lies under the retina, which is the “film” in the back of the eye that “takes the picture” of objects you look at. BSC is fairly rare form of inflammation affecting both eyes of men and women, usually starting in middle age.
What causes birdshot chorioretinopathy?
Birdshot chorioretinopathy (BSC) is strongly related to genetics. Most people with BSC have inherited a cell protein called HLA-A29. However, most individuals with HLA-A29 do not develop BSC; it appears to be triggered by an external event, such as an infection that “awakens” the immune response, which then abnormally attacks the eyes. BSC is most common in people of European ancestry.
What are the symptoms of birdshot chorioretinopathy?
Birdshot chorioretinopathy (BSC) usually presents with the slow-onset of floaters and blurred vision in both eyes. The floaters appear as tiny floating dots, which move or “float” in the vision and are seen especially well in bright environments. Shimmering lights may also be reported. Some patients note difficulty seeing at night. Symptoms may be very bothersome despite normal vision as measured on the eye chart. Over many years without treatment, the vision deteriorates further with loss of contrast, color vision, peripheral vision, and central vision. The symptoms vary from person to person and some have more rapid and severe deterioration than others.
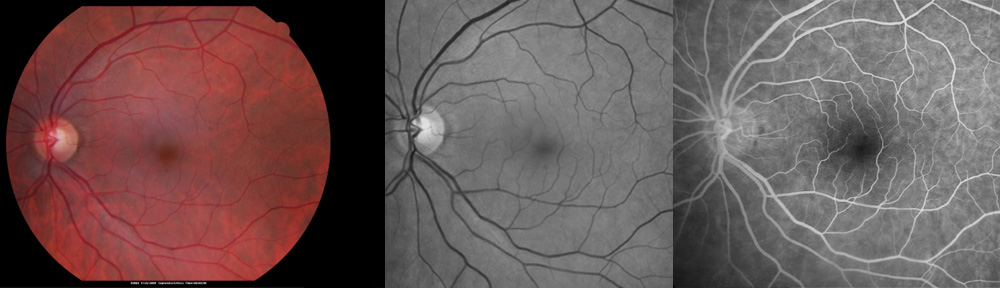
How is birdshot chorioretinopathy diagnosed?
The diagnosis of birdshot chorioretinopathy (BSC) may be delayed due to the slow onset of symptoms and the subtle findings on the eye exam. A retinal specialist or uveitis specialist may be needed to perform sophisticated testing and make the diagnosis. Inflammation may be detected in many different parts of the eye, but the most typical findings include numerous pale spots inside the back of the eye. Blood testing for HLA-A29 is positive in the vast majority of patients with BSC. However, not all patients with uveitis who are positive for HLA-A29 have birdshot chorioretinopathy. Therefore, it is necessary to exclude other diseases that may simulate BSC including lymphoma, sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, syphilis, and cancer medications such as pembrolizumab and others.
How is birdshot chorioretinopathy managed?
Birdshot chorioretinopathy (BSC) usually requires management by an experienced retinal or uveitis specialist. In most cases, systemic treatment (pills or injections into the skin) are needed to control the inflammation. In a small subset of patients, localized treatment to the eye is sufficient. This is more often the case in older patients at onset of symptoms. When pills are used, the eye doctor frequently coordinates medical care with the expert assistance of a rheumatologist (a medical specialist with expertise in auto-immune diseases, like rheumatoid arthritis). In BSC the rheumatologist monitors the patient for medication side-effects that may develop outside the eyes. In many cases, the uveitis may be long-lasting. In these cases, years of therapy are needed to preserve vision.
Your doctor will choose from a variety of medications. Steroids (pills, eye drops, and injections) may be used at the start of treatment to gain rapid control of inflammation. However, long-term steroid treatment in high doses is usually avoided to prevent side-effects of steroid therapy. For long-term control methotrexate (MTX) pills or skin injections may be given weekly. MTX has a long record of safety and is affordable. If MTX fails or causes side-effects (liver or bone marrow), CellCept is another suitable medication, though it may cause diarrhea. Cyclosporin has been used effectively, but is fraught with a high incidence of problems with hypertension (high blood pressure) and kidney toxicity. Humira is a new biologic treatment given as an injection into the skin every two weeks. It has been approved by the FDA for treatment of uveitis, such as BSC. All medications used to treat BSC may have adverse effects and must be monitored for effectiveness and safety in a given patient.
Birdshot chorioretinopathy is a serious eye problem and may result in loss of vision or blindness. However, by seeing your eye doctor and taking the medications exactly as recommended, damage to your vision can be minimized.
For a telemedicine consultation with Dr Pautler, please send email request to spautler@rvaf.com. We accept Medicare and most insurances in Florida. Please include contact information (including phone number) in the email. We are unable to provide consultation for those living outside the state of Florida with the exception of limited one-time consultations with residents of the following states: Alabama, Arkansas, Connecticut, Georgia, Minnesota, and Washington.
Copyright © 2020-2023 Designs Unlimited of Florida. All Rights Reserved.